🚀 Kickstart to DevOps♾️Introduction and Overview
Beginner's Guide to trending culture of software development lifecycle
👉 Quick Intro
Dev+Ops is actually a combination of two words: Development and Operations.
It is a culture/process to build and deploy applications by following continuous integration and continuous delivery (deployment) - CICD.
DevOps follows a few practices which are nothing but steps in order to do it.
The main purpose of using DevOps is to decrease software development life cycle time and to provide delivery with high software quality.
It is better to know Agile Methodology so that you can understand DevOps better. [optional] [check out my blog on Agile Methodology]
In simple words DevOps is not any tool, language, or framework, it is just a method or process that is followed while developing an application to build and deploy in real-time.
Now what is CICD ♾️ ???? let's see
Imagine you're baking a delicious cake. 🍰
Continuous Integration (CI): CI is like baking your cake step by step, and after you finish each part, you have a special taste tester, let's call them the "Taste Checker," who takes a little bite to make sure that part tastes yummy and is just right. If it doesn't taste good, you fix it immediately. This way, you know that every part of your cake is super tasty.
Continuous Delivery (CD): CD is like getting your cake ready to share with your friends. You have another friend, let's call them the "Cake Deliverer." When you say your cake is ready, the Cake Deliverer takes it and brings it to your friends' party. If your cake doesn't taste amazing, the Cake Deliverer won't take it. But because of CI, you're pretty sure it's always perfect when you ask the Cake Deliverer to bring it to the party.
👉 Role of DevOps Engineer 🧑💻
Create GitHub repositories for developers collaboration while developing applications.
Create an infrastructure that includes servers, pipelines, and gateways using Terraform or any other in the cloud
Manage configurations like version of software or packages, storage required, etc.
Setup servers and database to run the application and store the data
Manage permissions for team members
Create CICD pipelines for build and deployment
Manage and monitor servers and applications
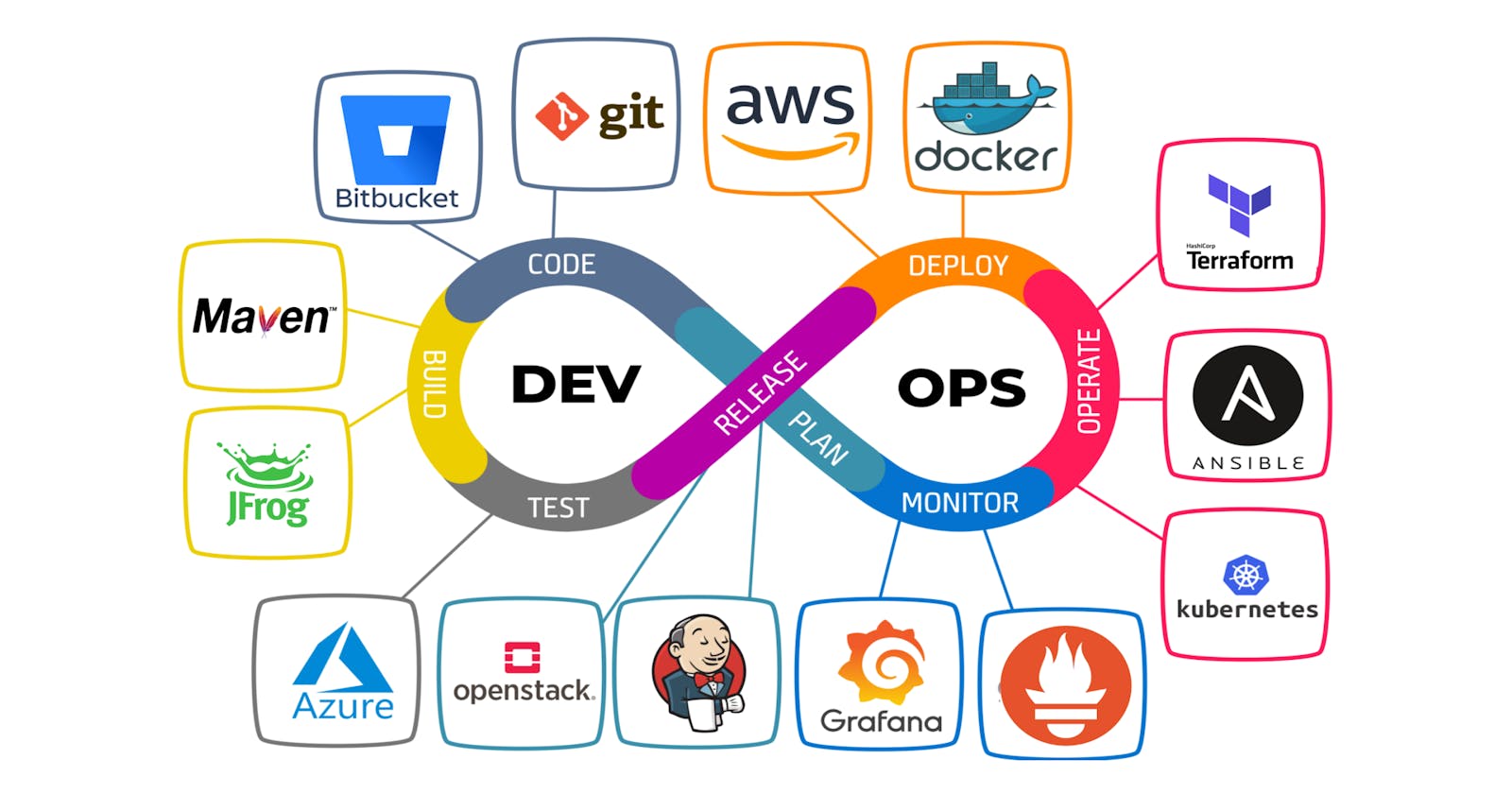
👉 Stages in DevOps 🛑
As you can see in the cover image, the infinity symbol is a kind of logo that represents CICD or DevOps, which has stages mentioned in it.
Plan - before starting software development, we plan things like features, and create tickets as per that feature.
Code - were actual development begins by developers
Build - after completion of a piece of code, the developer builds the application into a single file
Test - test the app or developed feature
Release - provide it to the operations team for deployment
Deploy - deploy app on servers
Operate - manage the app so that it won't get down, even if it goes then fix it
Monitor - see the metrics or logs of application
👉 Tools in DevOps ⚙️

GitHub or Bitbucket: used to store project source code
Maven or npm: used to compile source code depending on the language that is used for development
SonarQube : used for code review/code quality checking
Nexus Repository or JFrog : artifactory repo server, used to store builds
Tomcat or JBoss : server to run application
Jenkins : automating build and deployment of project on the server
Ansible : used to automate configuration management
Terraform : used to create infrastructure in cloud
Docker : containerization - package, build & run application in any machine
Kubernetes or EKS : orchestration - manage docker containers
Prometheus : monitoring & alerting too
Grafana : visualization tool
ELK Stack : Elastic Search, Log Stash, Kibana - monitor app logs
[each tool will be explained in detail in upcoming blogs]
👉 Flow of DevOps 🔥

Developers from anywhere can collaborate and integrate their code on GitHub
Whenever a new change is made in the GitHub repository, Jenkins triggers the pipeline
Pipeline will clone the repo, and the code quality check will be done
If passes the code quality check then build the application and store it in an artifactory
Docker image of that build is created and orchestrated by Kubernetes and deployed on server
👉 Benefits of DevOps ✅
Faster Delivery: DevOps shortens the time it takes to develop and release software, making it available to users faster.
Higher Quality: Automated testing and monitoring reduce the number of defects and enhance the overall quality of software.
Improved Collaboration: DevOps encourages better communication and cooperation among team members, fostering a more productive work environment.
Efficiency: Automation eliminates manual, time-consuming tasks, reducing the chances of errors and improving efficiency.
Scalability: DevOps provides the tools and practices needed to scale applications and infrastructure to meet growing demands.
👉 Conclusion 🛑
DevOps is not just a buzzword; it's a game-changer in the world of software development. While it may seem overwhelming at first, especially for beginners, the principles and practices of DevOps are designed to make software development more efficient, collaborative, and responsive to user needs. As you embark on your DevOps journey, remember that it's a cultural shift as much as a technological one. Embrace collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement, and you'll find that DevOps can empower you to deliver better software faster.
Happy DevOps journey! 👋